Why the future of aviation safety is solid: New C-Band Weather Radar WRS300
There’s no doubt about it: Weather is getting more extreme and less predictable around the world. Airports work hard to ensure safe and efficient flights and depend on accurate weather radar to make critical decisions. Today, major improvements in weather radar technology and design can help you change the game for aviation safety.
Solid-state power amplifiers for new weather radar
In June, we announced the Vaisala C-Band Weather Radar WRS300 which uses solid-state power amplifiers (SSPA) instead of traditional tube-based transmitters. Why does this matter? SSPA makes it possible to create an all-new C-band weather radar which provides large area coverage and exceptional accuracy, all in a compact, low-maintenance package. The result is improved assessment, prediction and preparation of adverse weather such as windshear at and around the airport, especially in the crucial terminal maneuvering area (TMA) on approach – more about this in our upcoming webinar.
The solid difference
Solid-state transmitters have been used widely in all kinds of radars in the past, but tube-based transmitters such as magnetron have been used to produce those high-powered weather radio frequency pulses. Today, Gallium Nitride components are widely available and are made for all radar bands, so Vaisala has been able to take advantage of solid-state transmitters in our radars. They also have low peak power with a high duty cycle, so they operate longer (translation: very little maintenance, much lower lifetime costs).
The advantage of peak power
SSPA provides high measurement sensitivity with significantly lower peak power than tube transmitters. Significantly more reliable and redundant components are used in the transmitter in order to produce this lower peak power, thus greatly improving the overall reliability. To maximize measurement sensitivity, Vaisala uses long pulses with pulse compression which we've had in-house for over 15 years with some very well-proven algorithms.
The result:
• Less stress to the sensitive receiver front end during the transmit pulse
• Enables the use of semiconductor limiters without radioactive discharge tube technology
• Easier and more reliable design of waveguide parts without a risk of arcing
• Less interference for other radiofrequency devices
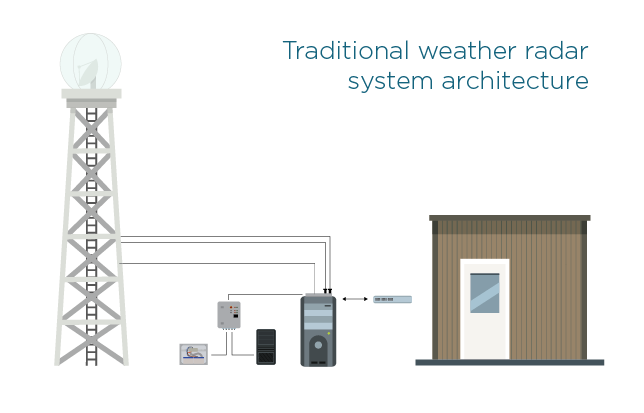
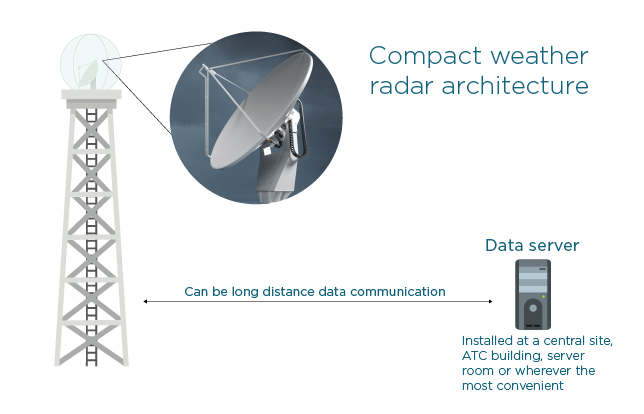
Major design enhancements
The new radar architecture is also a great improvement. Figure 1 shows a typical setup with a magnetron radar: A 20-meter tower with the antenna pedestal at the top, plus a separate container with the transmitter cabinet, receiver, and electronics. It is very expensive to set up and maintain.
As Figure 2 shows, we’ve moved all the electronics to the back of the antenna for a drastically simplified signal path. This is key for better performance and reliability with lower costs.
New algorithms and dual transmitters
We have patented algorithms to improve all radar performance. With pulse compression and solid-state technology, we’ve added new algorithms to further improve performance plus continuous calibration. This means you don't lose any of the signal in the wave guides, and it has a higher average transmission power. So that's how you get better measurement performance for wind, rain and other types of precipitation.
WRS300 is also much more reliable because, unlike radars that have a single tube-based transmitter, the C-band has two independent transmitters: one for the horizontal channel, the other one for the vertical channel, both acting as independent transmitter modules. Even if you lose one of them, the radar will continue transmitting with very high transmission power.
As the highest-performance radar of its time, C-Band Weather Radar WRS300 delivers high-resolution weather forecasting information that differentiates between snow, hail, sleet, graupel and rain, and helps air traffic controllers, pilots, meteorological observers and forecasters to make better decisions and improve the safety of your airports in all conditions.
Learn more about WRS300 for Aviation and get your free copy of our new eBook: Powerful performance with SSPA


Add new comment