Polyamide (Nylon) Fiber Production
Introduction
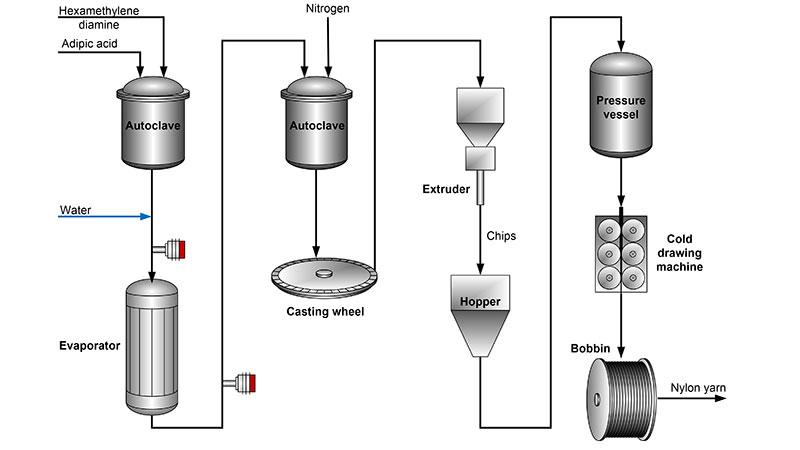
Nylon 6-6 was the first commercially made all-synthetic fiber. The product resulting from the polymerization reaction of adipic acid and hexamethylene diamines is called Nylon 6-6. The name comes from the molecular chains of the two raw chemical components, containing six carbon atoms each.
Chemical curve: Nylon salt R.I.per Conc% b.w. at Ref. Temp. of 20˚C
Application
The reaction between adipic acid and hexamethylene diamine produces hexamethylene diammonium adipate, commonly called nylon salt. It is essential for the material to be polymerized so that high quality fibers, with very few impurities, can be achieved.
Different types of nylons can be made by using a variety of processes.
In the batch process, the hexamethylene diammonium adipate solution is concentrated in an evaporator and acetic acid is added to stabilize the chain length. After evaporation, the salt solution is heated and the remaining water removed. TiO2 dispersion is added and the polymerization takes place. After the polymerization is completed, the molten viscous polymer is forced out through the bottom of the autoclave, onto a casting wheel and extruded as rapidly as possible.
Nylon is also produced by continuous processing, which is more economical for large quantity production, whereas the flexibility of the batch process allows end-product variations.
Nylon 6, or caprolactam, is a polymeric fiber derived from only one constituent, caprolactam. It has a lower melting point than nylon 6-6 but has superior dyeability, elasticity and resistance to light, etc. Other types of nylons also have useful differing properties.
Typical end products of polyamide fiber, nylon salt
- Synthetic fibers
- Nylon fibers
- Nylon 6
- Nylon 6-6
Instrumentation and installation
Vaisala Polaris™ PR53GP Process Refractometer is used to monitor and control the nylon salt, caprolactam and polymer solution concentrations.
The refractometer is installed after the evaporator to ensure the target concentration is achieved. Another refractometer can be installed before the evaporator for real-time monitoring of the evaporation efficiency. The refractometer provides Ethernet and 4-20 mA output signals that can be used for automatic control of evaporation, for instance, by regulating heat-flow or the feed to the evaporation.
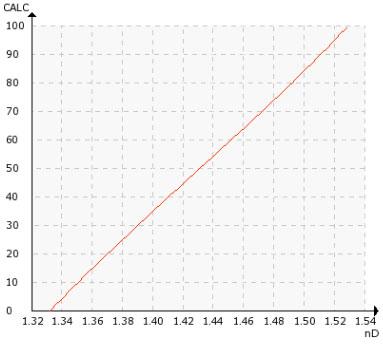
Typical refractive index measurement range for nylon salt is 1.3300-1.4100, and the process temperature is 60 ºC (140ºF). Typical refractive index measurement range for caprolactam is 1.3370-1.3570.
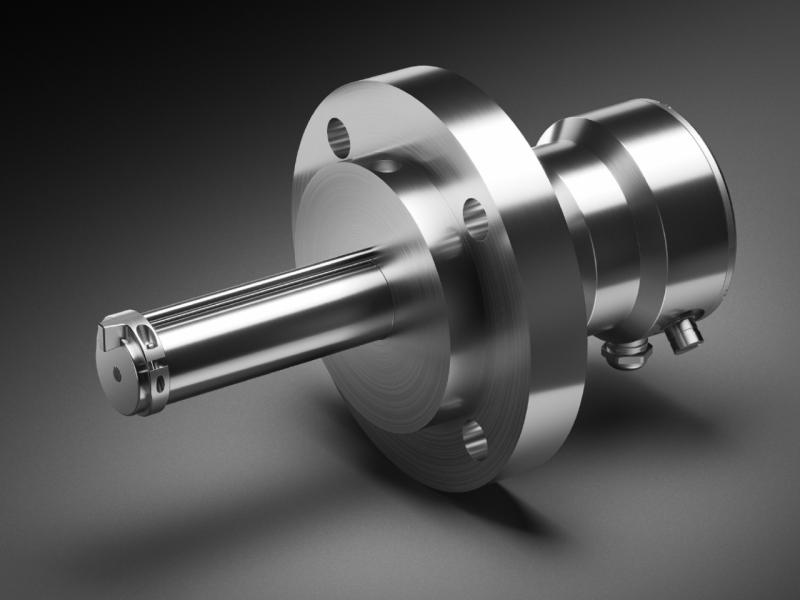

Vaisala Polaris™ PR53GP Process Refractometer
The Vaisala Polaris PR53GP Process Refractometer is a heavy-duty instrument with non-weld body construction for diverse applications. The PR53GP can be installed directly into a tank or large pipelines, using either a standard ANSI, DIN or JIS flange connection, or clamp connection.
User Interface
Vaisala Polaris process refractometers are compatible with the Indigo platform, offering plug-and-play connectivity, user-friendly interfaces and service and configuration tools. The Indigo520 transmitter adds a physical user interface, data logging, advanced diagnostics, automatic wash control, and access to measurement settings and parameters.
Measurement range
Refractive Index (nD) 1.3200 – 1.5300, corresponding to 0-100 % by weight.