Ammonia Removal in Water Treatment
Introduction
Small amounts of Ammonia (NH3) is present in aquifer naturally. Higher content is considered an impurity, often resulting from sewer backflow and drainage system problem, runoff in agricultural areas where it is used as a fertilizer, inadequate wastewater and solid waste disposal and treatment.
Ammonia is undesirable in water because ultimately it gets converted into nitrites and nitrates which can cause vitamin deficiency, and if combined with other components can cause cancer. Moreover, elevated ammonia concentration can create favorable conditions for intensive growth of aquatic organisms, including algae, which leads to deterioration of commodity water quality, especially its clarity, smell, taste as well as bacterial contamination.
Application
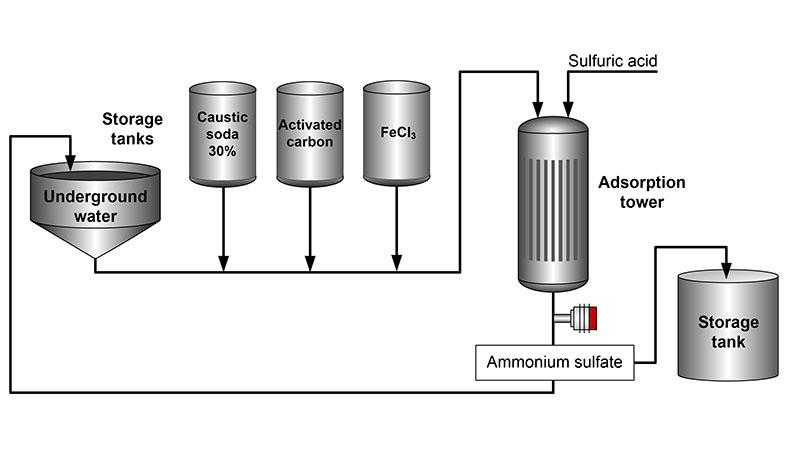
For ammonia treatment to underground water caustic soda (30 %), activated carbon and ferric chloride (FeCl3) are used. Caustic soda is a chemical reagent, pH-regulating, ion exchanger regenerating agent, catalyst, etching or cleaning agent. It leaves no residual colour.
Activated carbon is used as filter media for dissolved organics, as well as for the removal of color-, tasteand odor-causing compounds. It helps to improve the adsorbing capacity of ammonia.
Ferric chloride is a coagulant used for the treatment of turbidity and for further removal of color, natural organic materials, and arsenic from the raw water.
The ammonia is stripped away from the process. Sulfuric acid (50 %) is used as a stripping medium. Sulfuric acid added to the adsorption tower converts ammonia into ammonium sulfate ((NH4)2SO4). Ammonium sulfate is an inorganic salt which has commercial value. Its most common use is as a soil fertilizer.
Typical end products
- Inorganic salt with a number of commercial uses, e.g. soil fertilizer.
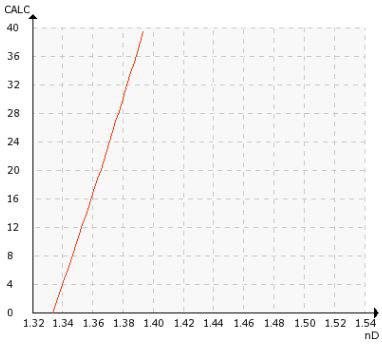
Chemical curve: Ammonium Sulfate, (NH4)2SO4. per Conc. % b.w. at Ref. Temp. of 20˚C
Instrumentation and installation
Vaisala Polaris™ PR53M Process Refractometer provides in-line and continuous measurement of ammonium sulfate concentration. If the concentration value is correct, ammonium sulfate can be stored for further use. If the concentration is out of specification, the product is recycled for further processing and the adsorption process is adjusted accordingly.
It is important to constantly monitor the ammonium sulfate concentration value in order to regulate the process correctly, to discharge or further recycle the product. Target concentration in this application is about 30 %.
The mounting point of the refractometer is at the outlet of the adsorption tower.

Vaisala Polaris™ PR53M Process Refractometer
Description
The Vaisala Polaris PR53M PTFE-Body Process Refractometer is for chemically aggressive solutions and ultra-pure fine chemical processes. The PR53M can be mounted to ½ inch process lines with a standard NTP-threaded connection, or optional pillar or flare fittings.
Measurement range
Refractive Index (nD) 1.3200 – 1.5300, corresponding to 0-100 % by weight.