Acid Wet Scrubbing of Ammonia-containing gas
Introduction
Ammonia is widely used in a variety of industries. Emissions of ammonia are of great concern as they contribute to several environmental problems including eutrophication and contamination of groundwater. Moreover, ammonia is very corrosive and may cause breathing problems at concentrations above 50 ppm and is considered poisonous in greater quantities.
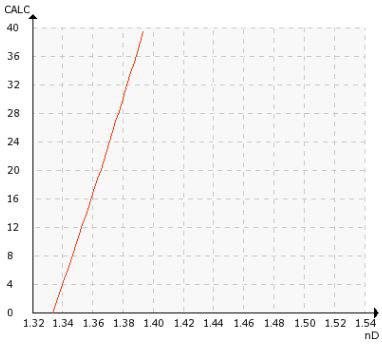
Chemical Curve: Ammonium sulphate R.I. per % b.w. at Ref. T of 20 °C.
Application
Wet scrubbing is used successfully to control ammonia emissions, achieving efficiencies up to 99 %. However, wet scrubbers create effluents that need to be treated and disposed.
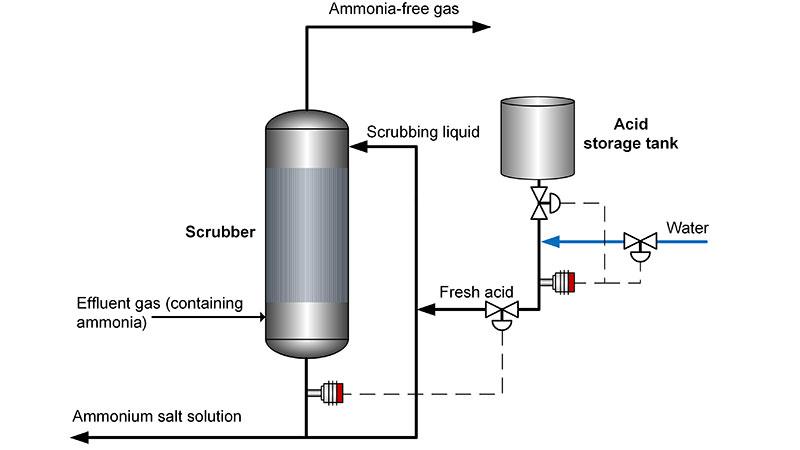
In acid scrubbing, a strong acid is added to the scrubbing liquid to react with the ammonia and to produce an ammonium salt, which can be safely discharged to a drain or wastewater treatment plant or sold as a liquid or solid fertilizer.
Typical ammonia scrubbers recycle liquid from the bottom to the top of the scrubber. This allows the scrubber to operate at reasonable wetting rates without the need for excessive acid addition or purge of liquid.
In continuous gas-liquid absorption systems, the concentration of the recycled solution is always controlled to ensure the proper acidic condition for scrubbing (usually a pH of 3 and 6) and to maintain the driving force by acid replenishment. The dosage of acid and water is controlled based on the pH and concentration of the scrubbing liquid.
Typical end products
- Ammonium salt of the acid, for example, ammonium sulphate, ammonium nitrate or ammonium dyhydrogen phosphate, with different uses, such as nitrogen fertilizers.
Instrumentation and installation
Vaisala Polaris™ PR53M Process Refractometer monitors continuously the concentration of the bottom product of the scrubber. The reading from the refractometer can be configured to show the preferred control unit, for example, Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) or density.
The refractometer’s signal is used to control automatically the concentration of the recycle line to the scrubber by the addition of fresh acid. This ensures the optimal conditions for ammonia absorption.
A second refractometer controls the dilution of the acid. The refractometer’s output signal can be used as feedback to control the water and acid feed valves to achieve the target concentration.
The design of the PR53M Process Refractometer makes it safe for use in processes involving corrosive chemicals, such as ammonium salts and strong acids.

Vaisala Polaris™ PR53M Process Refractometer
Description
The Vaisala Polaris PR53M PTFE-Body Process Refractometer is for chemically aggressive solutions and ultra-pure fine chemical processes. The PR53M can be mounted to ½ inch process lines with a standard NTP-threaded connection, or optional pillar or flare fittings.
Measurement range
Refractive Index (nD) 1.3200 – 1.5300, corresponding to 0-100 % by weight.